
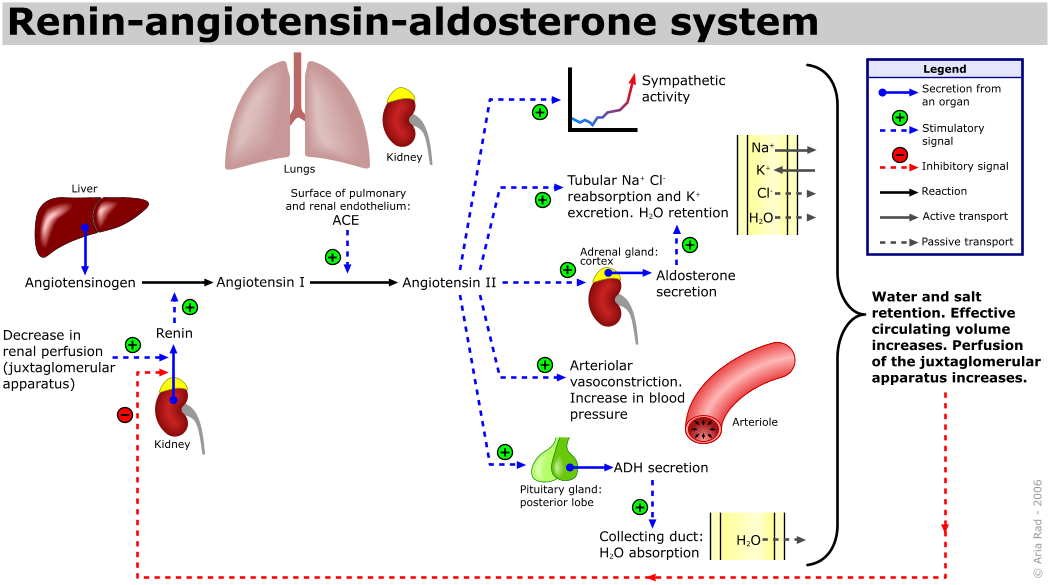
How are aldosterone levels controlled?Īldosterone is part of an elaborate group of linked hormones, enzymes, proteins and reactions called the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which helps regulate blood pressure. Indirectly, aldosterone also helps maintain your blood’s pH (acid-base balance) and electrolyte levels. Aldosterone’s effect on sodium increase causes your body to retain water in your blood, which increases blood volume.Īll of these actions are essential to increasing blood pressure levels to a healthy range once they drop.Aldosterone signals certain organs, like your kidneys and colon, to increase the amount of sodium they send into your bloodstream or the amount of potassium released in your urine (pee).Aldosterone contributes to this important function in a few ways: What is the function of aldosterone?Īldosterone’s primary function is to help regulate your blood pressure. If your body has too little or too much aldosterone, it can impact your health. These signals tell your body what to do and when to do it. Hormones are chemicals that coordinate different functions in your body by carrying messages through your blood to your organs, muscles and other tissues. They’re a part of your endocrine system and produce hormones that help regulate several important bodily functions. Your adrenal glands are small, triangle-shaped glands that are located on top of each of your two kidneys. Aldosterone also helps control the amount of water your kidneys reabsorb this increases blood volume and also impacts blood pressure. Electrolytes are minerals that help balance the amount of fluids in your body and keep your nerves and muscles functioning properly. Aldosterone (ALD) is a hormone your adrenal glands release that helps regulate blood pressure by managing the levels of sodium and potassium in your blood.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
